We propose a motion estimation method solving for the first time the complex problem of 3D winds field recovery from satellite image sequences. In order to manage incomplete observations, physical knowledge on 3D mass exchanges between atmospheric layers have been introduced within an optical flow scheme.
The estimator is based on a functional minimization. The data term relies on a model which describes the dynamics of an interacting stack of atmospheric layers. This model applies on a set of sparse pressure difference images related to the different atmospheric layers. A method is proposed to reconstruct such observations from satellite top of cloud pressure images and classification maps. To overcome the problem of sparse observations, a robust estimator is introduced in the data term. The data term is combined with a smoother that preserves the bi-dimensional divergent and vorticity structures of the three-dimensional flow and reinforces regions of homogeneous vertical winds.
Furthermore, a 3D graphical interface is proposed to visualize the horizontal and vertical components of the displacement of each layer. The wind fields are displayed in a physical 3D coordinate system. This system is deduced from pixel coordinates and altitudes estimated from the top of cloud temperature images. Smooth surfaces defining layer vertical boundaries are reconstructed through an altitude extrapolation scheme. An
evaluation of the system is performed with M´et ´eosat image sequences of top of cloud pressure.
References:
P. Héas, K Krissian, E. Mémin, A. Szantai. Reconstruction and visualization of 3D wind fields from satellite image sequences. 15th Satellite Meteorology and Oceanography Conference of the American Meteorological Society, Amsterdam, Netherlands, September 2007.
Software:
1- P. Héas, E. Mémin, N. Papadakis. Layers motion estimation methods (with physical coupling between layers), Fluid Project deliverable 4.1a, 2007 .![]() "download"
"download"

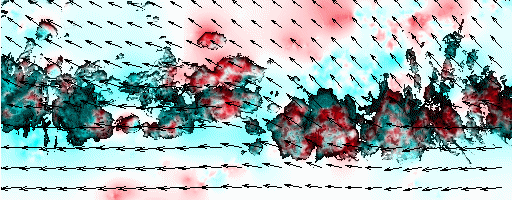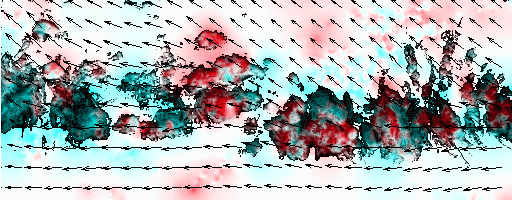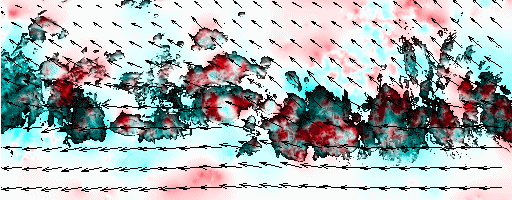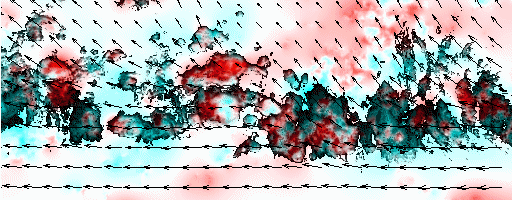
Cloud pressure difference images of the highest layer & Estimated horizontal wind vectors which have been superimposed on the images range in the interval [0,10] m/s (Images are over the Gulf Guinea the 5-June-2004 from 13h30 to 14h15 UTC). Retrieved vertical wind maps on the highest layer lower boundary have been superimposed on the pressure difference images. Vertical winds range in the interval [-0.5,0.5] m./s


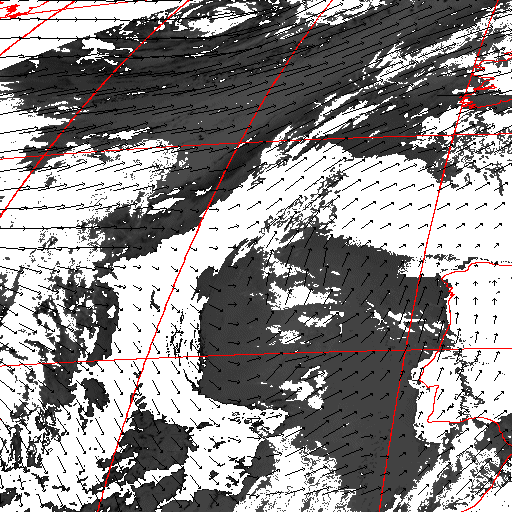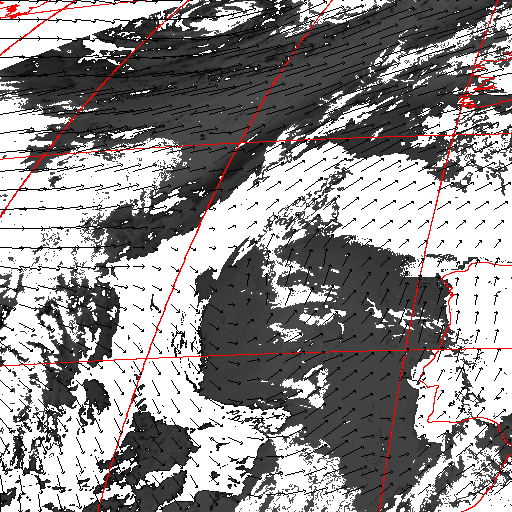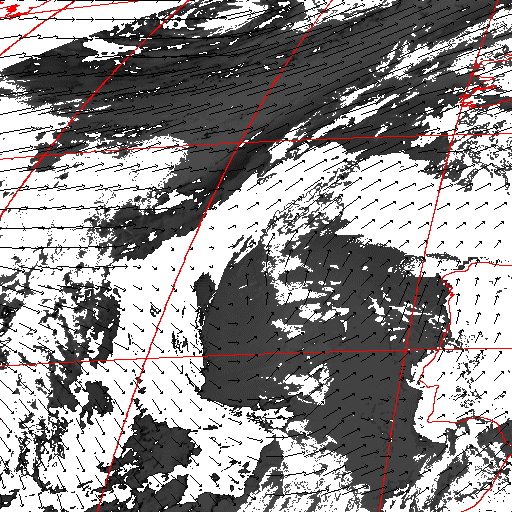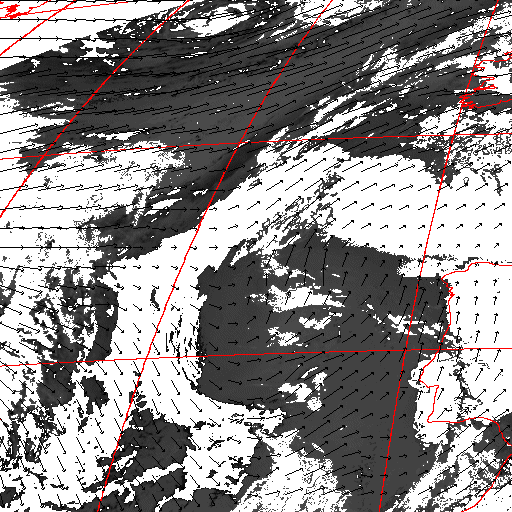
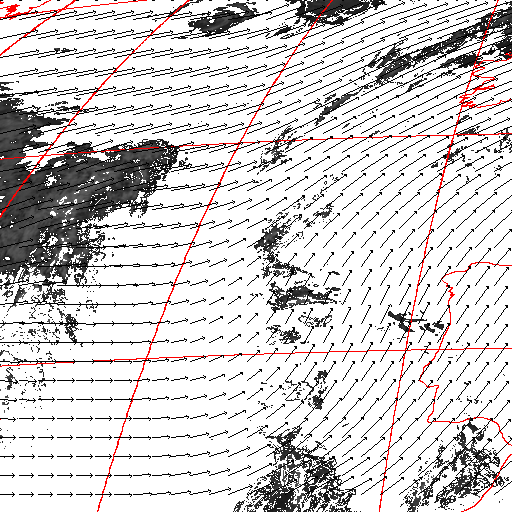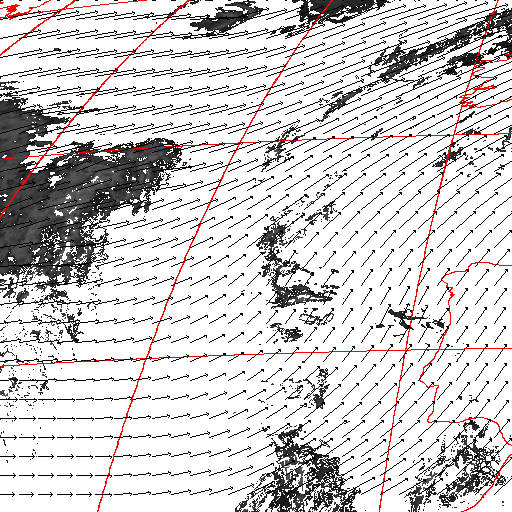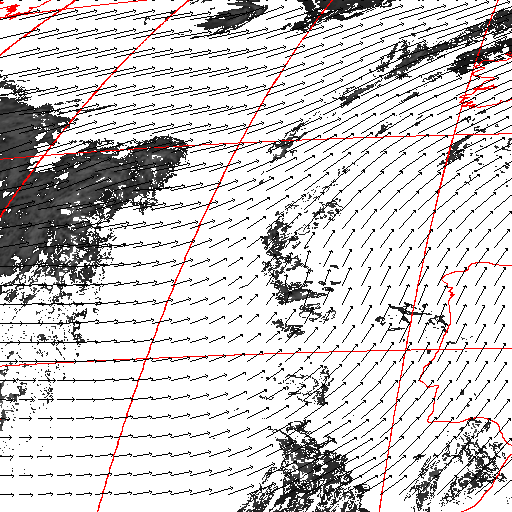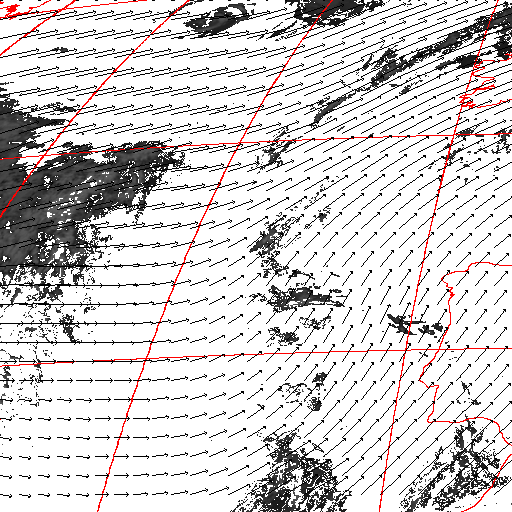
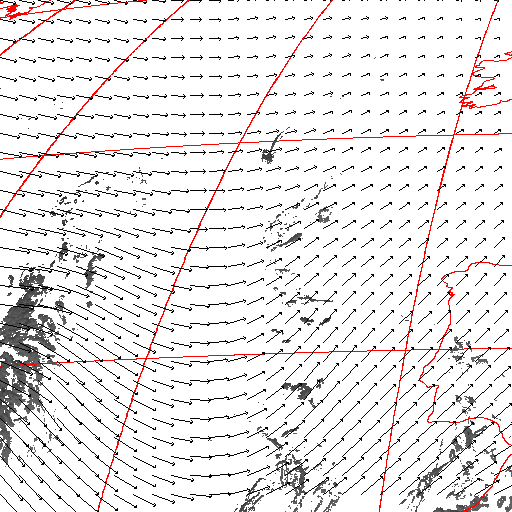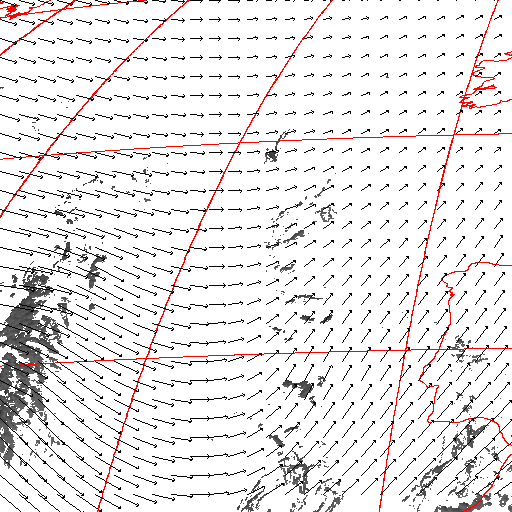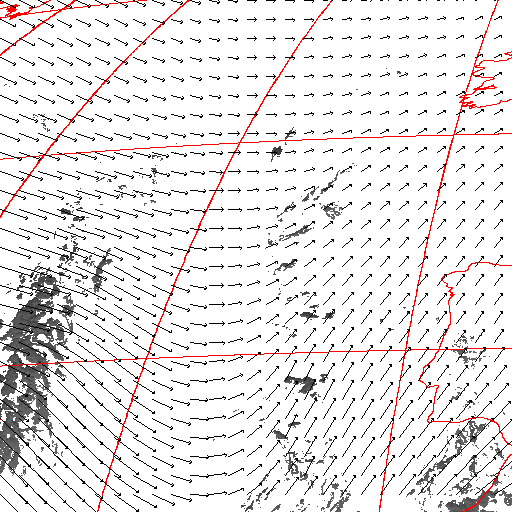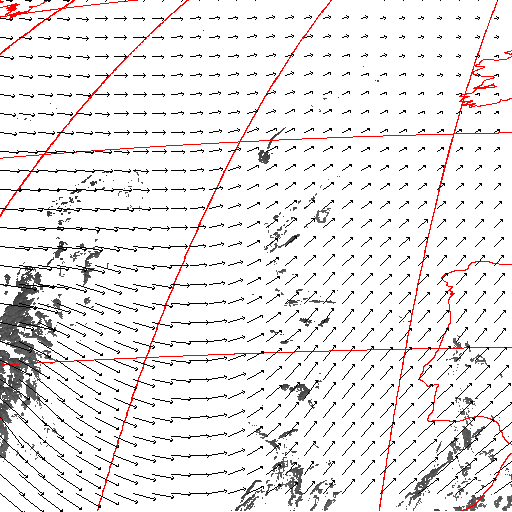
low horizontal wind intermediate horizontal wind high horizontal wind
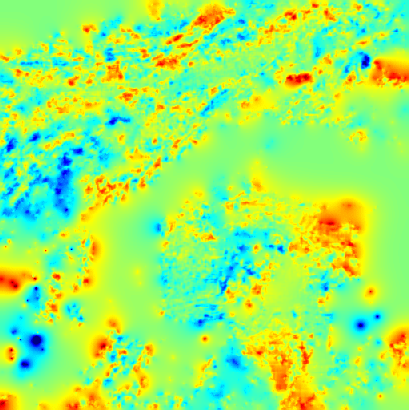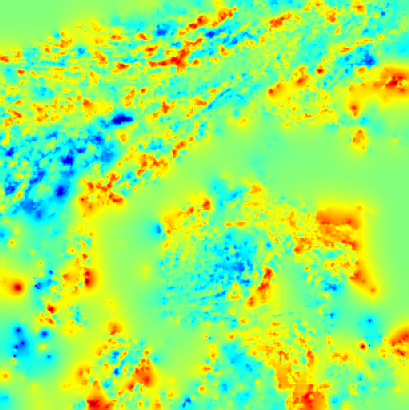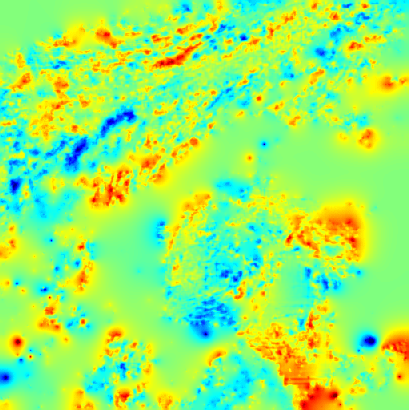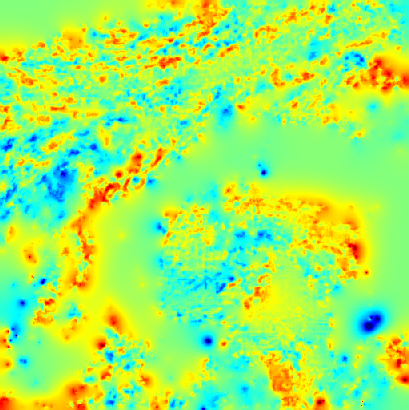
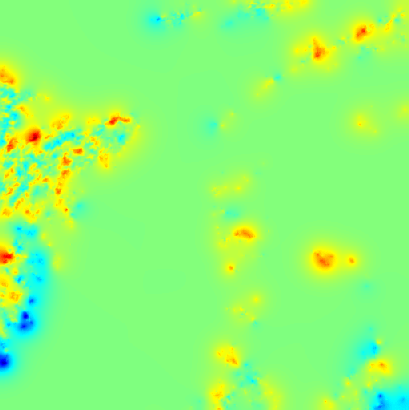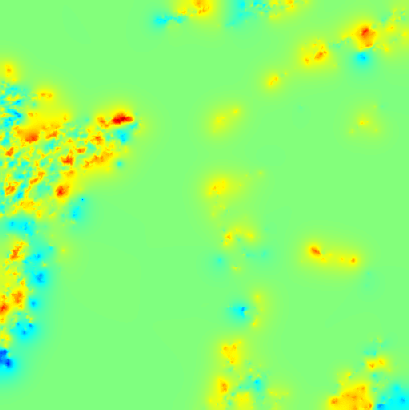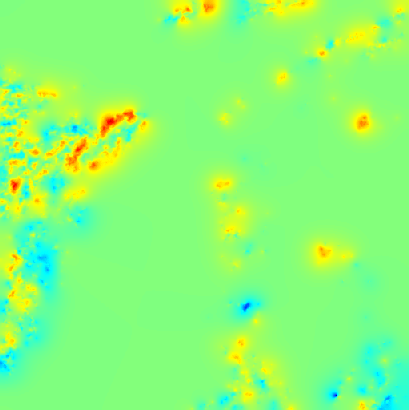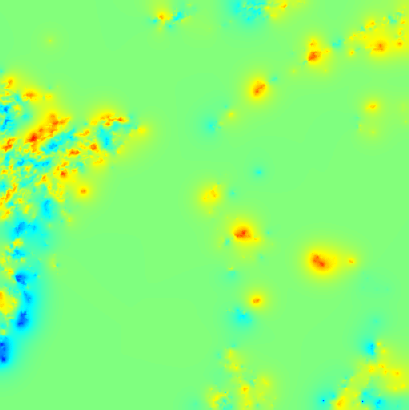
low altitude vertical wind high altitude vertical wind
Horizontal and vertical winds in correspondence to cloud pressure difference images (over the north Atlantic Ocean the 5-June-2004 from 12h00 to 13h00 UTC) related to the high (right), the middle (middle) and the low (left) layers. Estimated horizontal wind vectors range in the interval of [0,15] m/s. Estimated vertical winds range in the interval [-0.2,0.4] m/s.


